Different parts of your brain control and affect your behavior, here’s a brief look at each of them and how they work:
Frontal Lobes:
Social skills(social appropriateness), emotions, judgment, empathy, time management, working memory, morality and character, executive planning and initiative. Responsible for immediate and sustained attention(When the frontal lobe cannot properly manage attention, conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder may develop). The frontal lobes identify problems and may send them to other brain regions for a solution.
Parietal Lobes:
Interprets language, words, sense of touch, pain, temperature, Interprets signals from vision, hearing, memory, spatial and visual perception and motor skills.
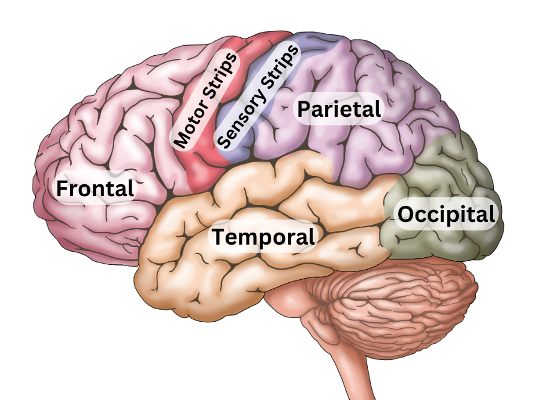
Temporal Lobes:
Help with word recognition, reading, language and emotion. The temporal lobes house the auditory cortex in close proximity to the hippocampus. Consequently, it is critical to the memory making process, especially verbal memories.
Ocipital Lobes:
Visual understanding and sight: see colors and recognize drawings and correctly identify objects. Reading, writing and spelling depend upon an accurate visual field.
Sensory and Motor Strips:
The functions of the primary motor cortex have been associated with skillful movements and smooth repetitive operations such as typing, playing musical instruments, handwriting and the operation of complex machinery and fluidity in speaking.
Bring back balance in your life with LENS Therapy
Brain Map Definitions
The colors on the surface maps represent the strength, or amplitude, of the EEG. Black and blue mean weaker brainwaves. Brighter colors such as olive, green, purple, red, yellow, and white mean stronger brainwaves (greater amplitude or greater dominant frequency, depending upon which topographic map your are viewing). It is very important to note that darker colors are associated with better functioning, and brighter colors are associated with mood, energy, thinking, movement, and overall pain problems.
Reading LENS Maps
The maps display the 21 functional sites that correspond to specific neuroreceptor site of the brain. Each neuroreceptor site contains what is called neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity is the range that allows our brains to receive, process and direct our brain functions to their most optimal level. Ideally we want Neuroplasticity around .35 to .70% light blue to black within each site.
The Mean Total Amplitude Graph
The Mean Total Amplitude is the average of all the information that we collected during a site placement and run. Each bar represents the average of the Delta, Theta, Alpha and Beta waves combined. We look at the difference between the light blue and black on each bar. The black is the energy in each site while the light blue is the neuroplasticity(flexibility) in each site. Ideally we want .35 to .70% light blue to black. The smaller the light blue portion means there is less flexibility in that specific brain site translating into the brain having to work harder and is often more reactive.
The Mean Dominant Frequency Graph
This graph is measured in Frequencies (cycles per second) broken down into different groups called Delta (.05-4Hz), Theta (4-8Hz) Alpha (8-12Hz) and Beta (12-42Hz). Each of these brainwave groups have a different functionality associated with it. Delta is attributed to deep sleep, Theta is associated with the dream state, creative state and subconscious state, Alpha is associated with meditation and being awake but not engaged while Beta waves are associated with engagement and activity while higher beta waves correlate to flight, freight or freeze mode.
From a LENS Mapping perspective we want to see the standard mean total amplitude map have a slope from 2± up to 25 MV with a decent amount of light blue to black and the mean Dominant Frequency with all the bars above 12 cycles per second (alpha wave and above) along with a healthy amount of light blue to black.